1st Demand Letter
The initial letter sent by USAC to recover funds from applicants or service providers who have committed program rule violations.
The E-Rate program, established by the FCC in 1996, provides discounts on certain services and products that are essential for schools and libraries to receive voice, video, and data communications. Expenses such as internet access, network cabling and equipment, network maintenance, and many other services can be discounted by up to 90% through this program. E-Rate discounts are calculated based on the percentage of students who are eligible for the Free & Reduced Lunch program or the level of poverty and location of the school.
Most elementary and secondary schools meet the criteria for E-Rate eligibility, including many private and religious schools. Public libraries and library systems can also receive E-Rate discounts, provided they meet the eligibility requirements of libraries.
Request a Consultation-01-1.jpg)
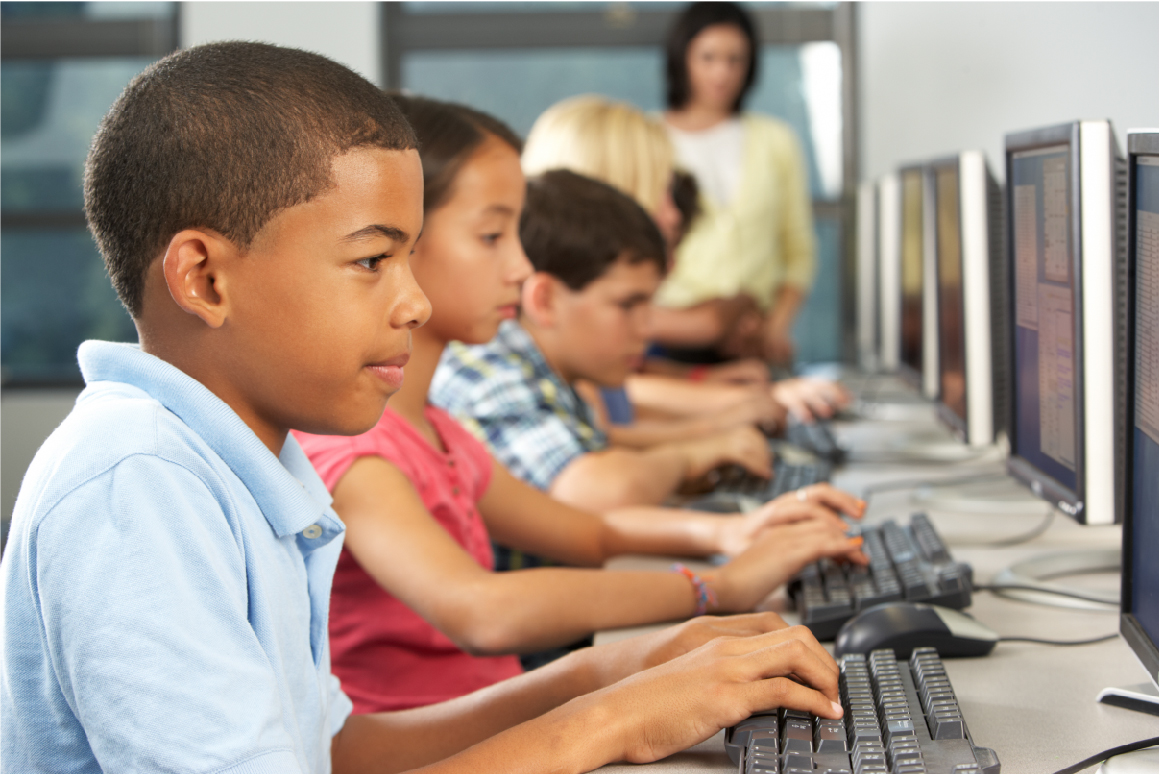
EdTechnologyFunds specializes in E-Rate consulting to help schools obtain funding for technology resources and build 21st Century learning environments.
With over 18 years of experience in E-Rate consulting, we have the background and expertise to provide comprehensive support for your district’s technology program needs. Our clients include school districts, charter schools, Head Start programs, and non-profit educational entities.

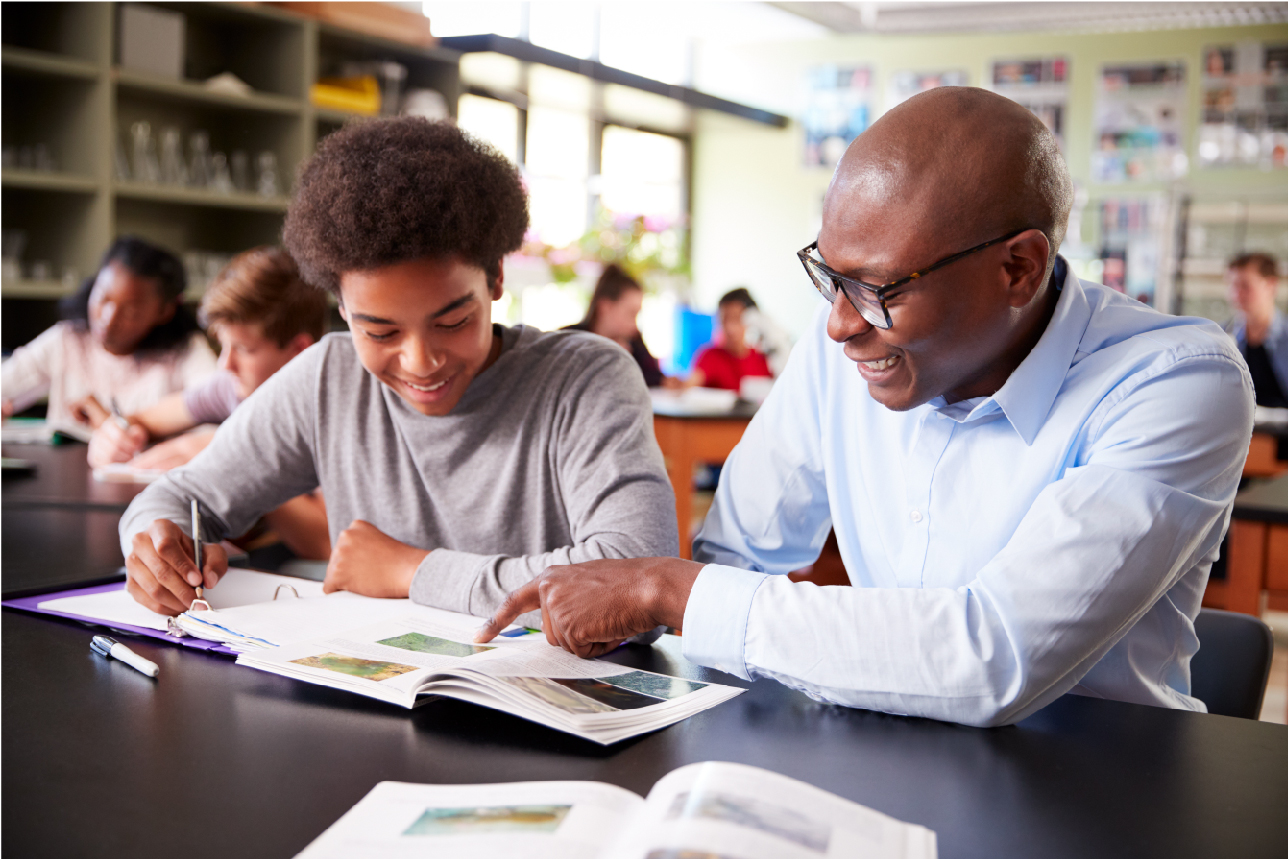
EdTechnologyFunds is also a leading E-Rate consulting firm for library WAN/LAN Infrastructure projects. We understand how libraries nationwide are transforming communities with E-Rate, and can help them maximize funding opportunities.
Library Directors, CIOs, IT Managers, and Administrators can count on us for the highest level support for E-Rate compliance and a white-glove service, alleviating the headaches that libraries typically experience in securing funding commitments.

The initial letter sent by USAC to recover funds from applicants or service providers who have committed program rule violations.
The Allowable Vendor Selection/Contract Date is the earliest date on which an applicant can sign a contract for contracted services or enter into an arrangement for tariffed (T) or month-to-month (MTM) services with a service provider. This date is always 28 days from the posting of the FCC Form 470 and/or the public availability of the RFP (if one is issued), whichever is later.
The time period an applicant is required to wait after posting the FCC Form 465 or FCC Form 461 (RHC) or FCC Form 470 (SL) before entering into any contract with a service provider. The purpose is to ensure a fair and open competitive bidding process for service providers.
Schools that choose not to use the National School Lunch Program (NSLP) participation numbers to calculate their E-Rate Program discounts may use certain federally-approved alternative mechanisms instead. These alternative discount mechanisms are not less stringent than the same measure of poverty established for the NSLP.
A follow-up letter to a 1st Demand Letter sent by USAC in an attempt to recover funds from applicants or service providers who have committed program rule violations.
An appeal is a request to reconsider a USAC decision. Appeals can be made to either USAC or the FCC. Appeals must be filed within 60 days of the original USAC decision. Requests for waivers of rules must be filed directly with the FCC.
The officer of a service provider company who is authorized to certify that data set forth in the FCC Form 498 is true, accurate, and complete. The 498 Company Officer has access to certify forms through the E-File system and occupies a position specified in the corporate by-laws (or partnership agreement), and would typically be president, vice president of operations, vice president of finance, comptroller, treasurer, or a comparable position. If the reporting entity is a sole proprietorship, the owner must sign the certification.
The entity applying for universal service support. In the Schools and Libraries Program the entity is a school, library, consortium, or other eligible entity that files program forms. In the Rural Health Care Program the entity is a health care provider or consortium.
A person who occupies a position specified in the corporate by-laws (or partnership agreement), and would typically be president, vice president for operations, vice president for finance, comptroller, treasurer, or a comparable position. If the reporting entity is a sole proprietorship, the owner must sign the certification. This person must review and certify the information reported on the FCC Forms 499-A/Q. The latest 499 Company Officer on file has access to certify forms through the E-File system.
A review of documentation and resources that verify the state of compliance with program rules.
The relevant authority with responsibility for administration of the eligible school or library who must certify the status of the entity’s compliance with the Children’s Internet Protection Act (CIPA) in order to receive universal service support.
An electronic clearing house and settlement system for exchanging electronic transactions among banking institutions.
A basic terminating component, which is normally located on a customer’s premises, is necessary to receive an end-to-end service because it provides translation of the digital transmission using the appropriate protocols. Equipment such as channel service unit/data service units (CSU/DSUs), network interface devices, cable modems, and gateways are considered basic terminating components.
See FCC Form 472.
A category of service on the Eligible Services List. Basic Maintenance of Internal Connections services cover the repair and upkeep of eligible products. Eligible repair and upkeep services include hardware, wire, and cable maintenance, along with basic technical support and configuration changes. The products must be eligible for discounts in order for their associated repair and upkeep services to be eligible.
A BEAR (FCC Form 472) Notification Letter is sent to the service provider and the applicant after a BEAR form has been processed by USAC.
The entity that receives the bill and pays for the supported service. A Billed Entity may be different from the physical location being supported.
See “Billed Entity Number.”
Run by USAC, and carried out by auditors trained in universal service and program audit requirements, these audits of beneficiaries and contributors serve to identify noncompliance with program rules and amounts of recoverable funds.
A response from a service provider (bidder) to a request for services.
The unique number assigned by USAC to each billed entity (school, library, or consortium) that pays for services.
The short name for the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). See “FCC.”
The FCC Form 471 is divided into six blocks. In a Block 4 worksheet, the applicant lists the entities receiving services and establishes the appropriate discount level.
Applicants applying for Category Two services in FY2015 or FY2016 will be able to request discounts up to $150 per student pre-discount per school, up to $2.30 per square foot pre- discount per library, or minimum (floor) of $9200.00 per school or library over a five-year period.
The FCC Form 471 is divided into six blocks. In a Block 5 funding request, the applicant provides details about services requested including service provider, category of service, and cost.
Internal connections services needed to enable high-speed broadband connectivity and broadband internal connections components. Category Two includes local area networks/wireless local area networks (LAN/WLAN), eligible broadband internal connections components, basic maintenance of eligible broadband internal connections components, and managed internal broadband services.
USAC Board of Directors
Corporate officer responsible for financial operations.
Beginning with FY2015, E-Rate Program recipients must cost allocate non-ancillary ineligible components that are bundled with eligible products or services, such as handsets included with telephone service or netbooks bundled with Internet access, including those components that previously would have fallen within the scope of components not requiring cost allocation as described in the 2010 Clarification Order.
A law that mandates certain Internet safety policy and filtering requirements for recipients of E-Rate Program discounts for services other than telecommunications services.
Services used to connect broadband or Internet to eligible locations, or services that provide the basic conduit access to the Internet. Telecommunications Services, Internet Access, and voice services are Category One services.
A helpline available to assist applicants and service providers. You can reach the helpline by visiting usac.org and clicking on “Submit a Question.” You can also fax us toll free at (888) 276-8736, or call us toll free at (888) 203-8100.
The process by which a funding commitment is reduced because of program rule violations.
An alternative provision to the normal requirements for annual determinations of eligibility for free and reduced price meals under the National School Lunch Program. Schools must have at least 40 percent of their students directly certified to qualify for CEP. Participating schools shall calculate their student eligibility for free and reduced priced lunches by the CEP multiplier. Schools are capped at 100 percent NSLP eligibility for purposes of determining their E-Rate Program discount.
This letter notifies both the applicant and the service provider of a COMAD. It contains a Funding Commitment Report which lists the Funding Request Numbers (FRNs) affected by the COMAD.
A requirement for applicants participating in the Rural Health Care or Schools and Libraries programs. The applicant conducts the process to select a service provider and order products and/or services. This process must be a fair and open competitive procurement.
An organization recognized by a regulatory authority (such as a state public utility commission) to provide telecommunications services to all requesting parties, or an organization that holds itself out to provide such services generally to the public for a fee.
A consortium (plural consortia) is a group of entities that apply together for funding.
An alternative provision to the normal requirements for annual determinations of eligibility for free and reduced price meals under the National School Lunch Program.
A consortium (plural consortia) is a group of entities that apply together for funding.
The date the contract is awarded to the service provider and signed by the applicant. Program rules state that this must be at least 28 days after an applicant posts FCC Form 465 or FCC Form 461 (RHC) or FCC Form 470 (SL).
A company or individual (non-employee of the entity) selected to perform certain activities related to the application process on behalf of the applicant or service provider for a fee. A Letter of Agency (LOA) or consultant agreement must be in place before the consultant undertakes these activities.
The date the contract between the applicant and service provider ends.
A law that requires federal agencies to transfer delinquent debts or claims to the Secretary of Treasury (Treasury) for further collection action. Unpaid obligations to the universal service fund are subject to the DCIA. In the event that a balance becomes over 120 days past due, (or 90 days past due for service providers), USAC will transfer the debt to the Treasury for further collection and enforcement actions.
A company that, based on the revenue reported on the FCC Forms 499-A/Q, is required to pay contributions directly to the universal service fund.
A 10-digit number that the FCC assigns to a business or individual that registers with the FCC. It is associated with an entity’s Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) and is required before filing FCC Forms 499-A/Q.
The employee(s) of a service provider company authorized to enter and modify company information on FCC Forms 498 and 499 through the E-File application. Also known as “authorized users,” these individuals are established by the Company Officer or General Contact.
A change to the SPIN featured on one or more FRNs that corrects a data entry error, reflects a merger or acquisition, or fixes some other type of error. It is not the result of a change to the actual service provider.
A demarcation refers to the point where a service provider’s network ends and where an applicant’s local area network (LAN) begins.
USAC is the FCC’s agent responsible for the administration, processing, filing and distribution of carrier revenue data for the Telecommunications Relay Services Fund — the cost recovery mechanisms for numbering administration and local number portability, and the universal service programs.
A worksheet that contains background information and notes the basis of an exception during an audit.
A web-based USAC tool used to access information related to applications, funding commitments, and disbursements.
Process that allows applicants to certify and submit forms online, eliminating the need for a paper form with an original signature.
Direct connections allow rural schools and libraries to share access to high-speed broadband services.
Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA), also known as No Child Left Behind (NCLB, 20 U.S.C. Section 7801 et seq.), provides the statutory definition of elementary and secondary schools.
The section of the FCC Form 471 where the applicant lists the entities receiving services and establishes the appropriate discount level.
Broadband distribution services and equipment needed to deliver broadband, a service eligible for E-Rate Program support starting in FY2015.
Starting with FY2015, all funding requests for any school or combination of schools within a school district qualify for a single school-district-wide discount rate.
Equipment located on school or library premises which staff members would use to access phone and/or Internet services: e.g., telephone handsets, cell phones, computers, and fax machines. End-user equipment is not eligible for E-Rate Program discounts.
Applicants and service providers must retain documentation related to the application for, receipt, and delivery of discounted services for at least 10 years from the last date of service delivery.
The FCC Report and Order that modernized the E-Rate Program and focused on high-speed broadband connectivity to schools and libraries (FCC 14-99).
EPC is the account and application management portal for the Schools and Libraries (E-Rate) Program. Applicants, consultants, and service providers participating in the E-Rate Program use this tool to manage program processes and to submit questions.
USAC’s online forms submission tool, available at https://forms.universalservice.org.
A regional public multi-service agency authorized by state statute to develop, manage, and provide services or programs to its component school districts. In some states, ESAs are called Educational Service Units (ESUs), Local Educational Agencies (LEAs), Board of Cooperative Educational Services (BOCES), or other similar designations.
The common term used in place of the Schools and Libraries Program. The E-Rate Program provides discounts to schools and libraries for eligible products and services.
The Billed Entity Applicant Reimbursement Form is an FCC form that schools and libraries submit to USAC after paying for services in full, to request reimbursement from the service provider for the discount on those services.
See “eligible telecommunications carrier.”
The Service Provider Annual Certification Form is an FCC form that service providers file annually to certify that they will comply with program rules and guidelines. This must be filed before USAC will pay invoices.
The Description of Services Requested and Certification Form is an FCC form that schools and libraries complete to request services and establish eligibility. The completed form is posted to USAC’s website for potential bidders to review, which opens the competitive bidding process for services desired that are eligible for discounts under the E-Rate Program.
The Service Provider Invoice Form is an FCC form that service providers submit to request reimbursement for discounted eligible services already provided to the schools or libraries on their customer bills.
The Services Ordered and Certification Form is an FCC form that schools and libraries use to report services ordered and discounts requested for those services.
The Certification by Administrative Authority to Billed Entity of Compliance with the Children’s Internet Protection Act Form is an FCC form that schools and libraries submit to certify that they are in compliance with the Children’s Internet Protection Act.
Filing Window The period generally between mid-November and mid-February, (prior to the start of the funding year) when forms filed are treated as having been received on the same day and are considered for funding before any other forms filed after the window closes.
See “General Contact.”
The Receipt of Service Confirmation Form is an FCC form that schools and libraries file to inform USAC that services have begun, to provide the status of their technology plan approval, and of CIPA compliance.
See “delegated users.”
This letter is issued by both the applicant and service provider to indicate that an FCC Form 486 has been successfully processed.
The Adjustment to Funding Commitment and Modification to Receipt of Service Confirmation Form is filed by schools and libraries to notify USAC of reductions to or cancellations of approved FRNs and/or changes to reported Service Start Dates or Contract Expiration Dates.
The Service Provider Identification Number and Contact Information Form is an FCC form that service providers must fill out in order to participate in any of the universal service programs. The form is used to collect contact, remittance, and payment information for service providers that receive universal service support.
See “CORES ID.”
See “498 Company Officer.”
The U.S. government agency that regulates interstate and international communications and oversees the universal service fund. In 1997, the FCC designated USAC to be the independent not-for-profit corporation to administer the universal service fund in accordance with its rules.
This act defines the financial operations requirements for government entities and this act would apply to the universal service fund as a result of the FCC Government Accounting Order.
The standards that apply to all government audits and will apply to audits of the fund and fund recipients effective with the Government Accounting Order.
The standards for government agencies that will apply to the fund effective with the Government Accounting Order.
An agency that reports to Congress, who asks the GAO to study the programs and expenditures of the federal government. It studies how the federal government spends taxpayer dollars, evaluates federal programs, audits expenditures and issues legal opinions.
The federal statute requiring access to information. Through the FCC, USAC is often called upon to respond to Freedom of Information Act requests.
The employee of a service provider company who filled out the FCC Form 498. This individual is listed on Line 8. The latest General Contact on file has access to submit and modify data in the E-file system, and to create delegated or authorized users.
A letter that contains USAC’s funding decisions on an applicant’s funding requests.
A unique number that USAC assigns to each funding request in a completed FCC Form 466 (RHC), FCC Form 462 (RHC), or FCC Form 471 (SL) application. This number can be found in an applicant’s FCDL or FCL.
Uniform minimum standards of and guidelines to financial accounting and reporting. The Financial Accounting Standards Board and the Governmental Accounting Standards Board are authorized to establish these principles.
In the Rural Health Care and Schools and Libraries programs, the funding year is a time during which program support is being provided. The FY begins July 1 and ends June 30 of the following calendar year.
Standards promulgated by the Auditing Standards Board (ASB) of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) These standards are recognized by state boards of accountancy and the SEC. GAAS consists primarily of 10 standards and accompanying statements on auditing standards or “SAS.”
A comprehensive child development program that serves preschool-age children and their families. Head Start facilities in some states are eligible for E-Rate Program funding.
A category of service on the Eligible Services List. Internet Access services are eligible basic conduit access to the Internet. Ineligible access includes content, equipment purchases, or other services beyond basic conduit access. However, selected services that are an integral component part of an Internet access service, (and other services designated as eligible by the FCC) may be eligible for discounts on interconnected VoIP, email service, and web hosting.
An outreach program established by USAC to help applicants and service providers by providing targeted customized training and outreach.
A company that provides Internet access service (also referred to as a service provider).
A law passed in 2010 to amend IPIA and enhance the federal government’s practices to measure and recover improper payments.
A statement or document that service providers submit to USAC after they have provided or completed service to the applicant. Invoices are submitted using FCC Form 474 (SL) or an FCC Form 463 invoice template (RHC).
A 2002 law that requires USAC to provide the FCC with accurate, timely information about improper payments to program beneficiaries. To comply, USAC created its Payment Quality Assurance (PQA) Program, which assesses specific payments made to beneficiaries in all four programs to determine if these payments were made in accordance with FCC rules. Using results of these assessments, USAC calculates estimates of improper payment rates and provides this information to the FCC.
A USAC-generated report sent to service providers upon receipt of the service provider’s invoices. The report breaks out which invoice line items were accepted and denied.
The lowest price that a service provider charges to non-residential customers who are similarly situated to a particular E-Rate Program applicant (school, library, or consortium) for similar services.
A category of service on the Eligible Services List. Internal Connections services are eligible products, such as routers, switches, hubs, and wiring. Eligible products are located at the applicant site and must be considered a necessity to transport information to classrooms or publicly accessible areas of a library. Product eligibility does not include services that extend across a public right-of-way beyond the school or library facility. Starting with FY2005, under the Two-in-Five Rule, eligible entities can only receive discounts for internal connections in two of every five funding years.
Order issued by the Commission to deny a petition for rulemaking, modify a decision, grant or deny a petition for reconsideration, or grant or deny an application for review of a decision. A second or third Memorandum Opinion and Order (2nd MO&O/3rd MO&O) may be issued.
The Item 21 Attachment to FCC Form 471 provides details on the products or services requested in FRNs that appear on the form.
An evaluation process used by applicants when a state files an FCC Form 470 and signs state master contracts with more than one service provider as a result. The applicant cannot simply choose one of these service providers, but must evaluate all eligible state master contracts and demonstrate why the service provider it chooses is the most cost-effective solution.
A written offer from a service provider and acceptance from the applicant that includes all the material terms and conditions and is legally binding.
Sometimes known as M&C, errors made in E-Rate Program forms that can be corrected after the forms are submitted to USAC.
A Letter of Agency (LOA) authorizes a consortium leader to apply for program support on behalf of each consortium member or a consultant to conduct specified activities on behalf of an applicant or service provider.
Parent company of USAC. Formed by the FCC as a not-for-profit corporation, NECA plays an important role in administering the FCC’s access charge plan, which helps ensure telephone service remains available and affordable in all parts of the country.
The LTSA, 20 U.S.C. Section 9121 et seq., (1996) provides the statutory definition of a library.
A voice, data, and/or video network that provide connections generally within an eligible school or library to other locations within the school or library.
This program provides school lunches to eligible students at a free or reduced rate.
A school building without classrooms or a library building without public areas. Examples of school NIFs include administrative buildings, bus barns, and cafeteria facilities. Examples of library NIFs include administrative buildings, bookmobile garages, and interlibrary loan facilities.
Part of the Department of Commerce, NTIA is responsible for telecommunications policy and provides telecommunications grants to various entities.
An order issued by the FCC that provides a penalty will be imposed on a carrier for violating an FCC rule or procedure.
A weekly newsletter that provides up-to-date program information, including important dates, tips regarding the application process, and other breaking news.
Adopted by the Commissioners primarily for fact-gathering; which is a way to seek comments from the public or industry on a specific issue.
The No Child Left Behind Act, 20 U.S.C. Section 7801 et seq., provides the statutory definition of elementary and secondary schools.
An announcement issued by the FCC to detail proposed changes to FCC rules and policies and seek public comment on the changes.
The non-discount portion (also called non-discount share) is the applicant’s share of the cost of the eligible E-Rate Program products and services, i.e., the cost to be paid by the applicant after the E-Rate Program discount is applied.
A division of the FCC that provides independent and objective audits and investigations relating to agency programs and operations.
Part of the Executive Office of the President, OMB reviews and approves FCC forms that are used by universal service contributors and universal service program participants, contributors and service providers.
The online version of FCC Form 472.
A code assigned to a specific authorized person at a specific billed entity to allow online form certification.
Equipment owned by a service provider but located at an applicant site. This equipment can be funded as Priority 1 if it meets the conditions of the Tennessee Test.
Master contracts designated by the FCC that are nationwide contracts that offer Category Two equipment.
A change to the SPIN featured on one or more FRNs made as a result of a change to the actual service provider.
The employee of company that filed an FCC Form 499-A/Q. This individual is listed on the FCC Form 499-Q Line 108 and FCC Form 499-A Line 203. The latest preparer on file has access to submit and modify data in the E-File system.
USAC’s own program, created to comply with IPIA, which assesses specific payments made to beneficiaries in all four programs to determine if these payments were made in accordance with FCC rules. Using results of these assessments, USAC calculates estimates of improper payment rates and provides this information to the FCC.
Provides greater visibility into pricing and technology choices by applicants. Information and pricing regarding the specific services and equipment purchased by schools and libraries shall be publicly available on USAC’s website.
Telecommunications services, Internet Access, and Telecommunications are known collectively as Priority 1, since they are considered primary and were funded first for funding years prior to 2015.
The compliance review process completed before funding commitments are made by USAC.
A notice issued by the FCC to notify the public of an action taken, a change made, or an upcoming event.
A report issued by USAC to the applicant detailing all invoicing activity (BEARs and SPIs) for all funding years that occurred during the previous quarter.
Issued by USAC to both the applicant and service provider to indicate that a filed FCC Form 471 has been received before the deadline and certified to allow ministerial and clerical corrections.
A form of solicitation for products or services that provides detailed information regarding those products or services and any additional details necessary for potential bidders to respond. Program applicants may incorporate RFPs in addition to the FCC Form 465 (RHC) or FCC Form 470 (SL).
A letter issued by USAC to applicants and service providers when changes to a funding commitment occur, usually as the result of a successful appeal.
The FCC Form 470 Receipt Notification Letter (RNL) is a letter issued by USAC to notify applicants that the FCC Form 470 has been successfully posted.
An RIDF is required when there has been a COMAD but funds have already been disbursed in excess of the revised commitment amount.ule violations.
A requirement that the FCC withholds action on an application, payment, and/or other requests for benefits when the universal service program participant is delinquent in non-tax debts owed to the FCC or other federal governmental agencies. This rule extends to applications for support and disbursements from the universal service fund, and requires that USAC suspend support to any company that shares a Tax Identification Number with a company that has a delinquent debt.
An entity is considered in Red Light status when the Red Light Rule goes into effect (the entity is delinquent). See “Red Light Rule.” USAC will not make any disbursements until the delinquency has been satisfied or payment arrangements are made. USAC takes into consideration the Red Light status of each entity at the FCC and will hold disbursements until the Red Light status is resolved.
Action taken by the FCC to return applications to USAC for further review.
One of the four universal service programs administered by USAC.
A detailed compliance review in addition to the normal PIA review that certain applicants must undergo before funding commitments can be issued.
The request for information sent to applicants when they have been chosen for Selective Review.
The date that services will end for an FRN. USAC may adjust this date if a program violation is identified or a deadline is missed.
The date that services will start for an FRN. USAC may adjust this date if a program violation is identified or a deadline is missed.
See “FCC Form 473.”
See “FCC Form 474.”
See “FCC Form 498″ or “Service Provider Identification Number.”
A contract that is competitively bid and implemented by a state government which can be used by eligible entities within the state to procure products or services, or both.
A company that participates in one of four universal service programs and provides telecommunications or Internet services, equipment, hardware, or software. Types of companies include but are not limited to: competitive access/competitive local exchange carriers (cellular, personal communications, or specialized mobile radio providers), incumbent local exchange carriers, interexchange carriers, Internet service providers, interconnected VoIP, local resellers (coaxial cable, non-traditional, operator, paging, messaging, payphone, prepaid card, private and satellite service providers), shared-tenant service providers or building local exchange carriers, SMR (dispatch), toll resellers, or wireless data providers.
A unique number that USAC assigns to each service provider once that service provider has submitted the FCC Form 498 to USAC. Every service provider is required to have a SPIN in order to participate in any universal service programs and to receive payments from USAC.
A change in the products and/or services originally requested in an FRN for the HCF or Pilot programs.
A state master contract, filed pursuant to a state-filed FCC Form 470, which can replace an existing state master contract that expires before the end of the upcoming funding year.
Discounts calculated for a group of individual schools and/or libraries that will share a particular service. They may be simple averages or weighted averages of the discounts of the individual entities.
A unique number that USAC assigns to ETCs that uniquely identifies that company based on its service area. Companies must have at least one SAC per state in which they operate, but can have more than one SAC within a state if they have more than one service area.
The letter issued by a USAC-certified Technology Plan Approver to approve an applicant’s technology plan. Approvals may also be issued electronically or posted on a website.
A plan prepared by a school or library that sets out how information technology and telecommunications infrastructure will be used to achieve educational goals, specific curriculum reforms, or library service improvements. Technology plans must be approved by a USAC-certified Technology Plan Approver. Beginning with Funding Year (FY) 2011, technology plans are only required for Priority 2 services.
The date that a USAC-certified Technology Plan Approver officially approves the technology plan (this is different from the technology plan creation date).
An agency or organization that has been certified by USAC to approve technology plans.
The date that a USAC-certified Technology Plan Approver officially approves the technology plan (this is different from the technology plan creation date).
The transmission, between or among points specified by the user, of information of the user’s choosing, without change in the form or content of the information as sent and received.
A category of service on the Eligible Services List. Telecommunications was added as a category of service on the Eligible Services List starting in Funding Year (FY) 2011. “Telecommunications” covers lit or dark fiber – and certain maintenance and installation costs not provided by a telecommunications carrier. Dark fiber is eligible if the applicant lights the dark fiber immediately; however, the costs for purchasing modulating electronics necessary to light the dark fiber are not eligible. “Telecommunications” does not appear as a separate category of service on program forms. We suggest that applicants considering these services list them as both telecommunications services and Internet access (see telecommunications services) on the FCC Form 470 to maximize the number and type of bids they receive. Applicants would then apply for discounts on the FCC Form 471 under “Telecommunications Services” if the fiber is provided by a telecommunications carrier. If not, applicants would apply under the “Internet Access” section.
Common carrier, as defined by the FCC, is an entity that provides telecommunications service including interexchange carriers, wireless carriers, and competitive local exchange carriers (also referred to as service provider).
A category of service on the Eligible Services List. Commonly available telecommunications services eligible for discounts include local and long distance wired telephone service; interconnected VoIP; cellular phone service, including text messaging and voicemail, and Centrex service. Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), Primary Rate Interface (PRI), T-1, T-3, and satellite services are also eligible. Telecommunications Services must be provided by a telecommunications carrier, that is, a company that offers telecommunications services on a common carriage basis.
The term derives from FCC Order (FCC 99-216, released Aug. 11, 1999) that specified the various conditions that an applicant must meet for on-premise equipment to be funded as Priority 1 services.
The Two-In-Five Rule states that beginning with Funding Year (FY) 2005, eligible entities will only be able to receive E-Rate Program discounts for Internal Connections Other than Basic Maintenance two out of every five funding years.
Under the authority of the 1996 Telecom Act, the FCC created universal service as well as the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC), the organization charged with administering universal service. Companies make contributions based on revenues from providing international and interstate telecommunications services.
An independent, not-for-profit corporation created by the FCC in 1997 to administer the four universal service programs which help provide communities across the country with access to affordable telecommunications services.
Money collected from telecommunications companies and dedicated to fulfilling the goals of universal service. Under the authority of the 1996 Telecom Act, the FCC created the USF as well as the Universal Service Administrative Company (USAC), the organization charged with administering universal service. Companies make contributions to universal service based on revenues from providing international and interstate telecommunications services.
The initial letter sent by USAC to recover funds from applicants or service providers who have committed program rule violations.A technology that allows users to make phone calls using the same line as an Internet connection.
Telephone services, such as Centrex, local and long distance, POTS, wireless telephone service, etc. are voice services. Starting with FY2015, support for voice services will be reduced by 20 percent a year.
This term is used for a group of funding commitment notifications that USAC issues to applicants and service providers on a given date. Waves are usually issued weekly.
This hotline allows members of the public to report suspected violations of program rules to USAC. These reports can be made anonymously and toll free by calling (888) 203-8100.
A voice, data, and/or video network that provides connections from within an eligible school or library to other locations beyond the school or library.